The World - Economic alliances
Economy
978-3-14-100890-6 | Page 47 | Ill. 3
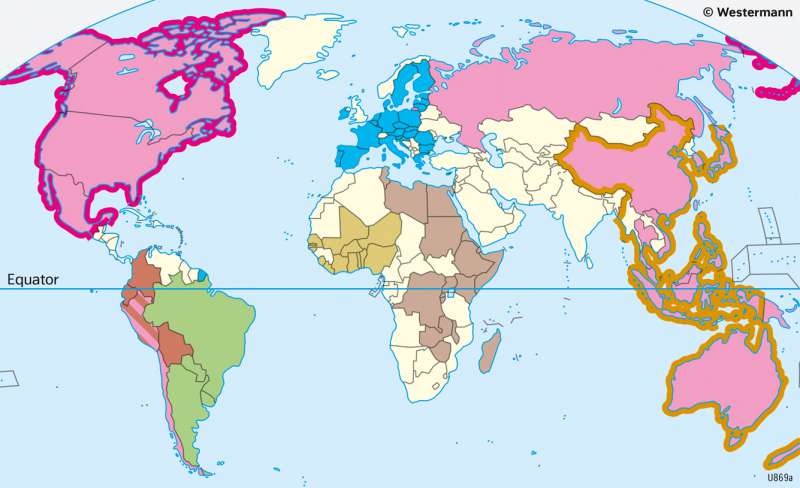
Overview
Multilateral free trade agreements have been promoted since the end of World War II: In 1947, the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) was signed by 23 states. Four years later, 12 European states formed the European Communities, the predecessor of the EU. In 1995, the then 76 GATT member states and the European Communities founded the World Trade Organisation (WTO) whose agreements substituted the GATT. Today, the WTO has 164 member states.
The European Union
The European Union (EU) emerged from the European Economic Community (EEC), whose twelve members decided to create a single European market based on the so-called "four freedoms" (free movement of persons, goods, services, and capital) in 1987. In 1993, the EU internal market was realised, and at the same time, with the Maastricht Treaties, the EEC became the European Union, which was joined by Sweden, Finland, and Austria in 1995. After a reform of the EU constitution and its institutions, comprehensive accession negotiations began in 1998, which led to the admission of ten new member countries in 2004 (Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Czech Republic, Slovakia, Hungary, Slovenia, Malta, Cyprus). They were later followed by Bulgaria and Romania (2007) and Croatia (2013). Currently, the EU has 27 member states, following a 2016 referendum in which a narrow majority of voters opted for the UK to leave the EU, which officially took effect on 1 January 2020.
African alliances
The Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS), founded in Lagos in 1975, is an economic and political association of currently 15 states that aims to create a West African economic and monetary union.
COMESA (Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa) is an organisation founded in 1994 by the countries of Eastern and Southern Africa to create a common market. Its headquarters are in Lusaka (Zambia).
North- and Latinamerican alliances
To the Andean Community ("Andean Pact"), founded in 1969 in Cartagena, Colombia, belong the countries of Bolivia, Colombia, Ecuador, and Peru. The headquarters of its organs are located in Bogotá. The aim of the pact is the economic, social and political integration of the countries. Chile, one of the founding members, withdrew under the dictatorship of General Augusto Pinochet in 1976, but today - like other South American countries - is one of the associated states.
Mercosur (Southern Common Market) is an economic alliance founded in 1991 by Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay and Uruguay, which in 2012-2016 also included Venezuela as a full member and several Latin American states as associate members. The aim is to create a single market and the seat of its organs is Montevideo.
The North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) was signed by the USA, Canada, and Mexico in 1994 and led to the creation of a free trade zone and the elimination of numerous tariffs. It was replaced in 2020 by the modified successor agreement USMCA (United States/Mexico/Canada Agreement).
Intercontinental alliances
APEC is an organisation of 21 states (including the USA, Mexico, Russia, China, Japan, South Korea, Chile, and Singapore) founded in Canberra in 1989, which advocates the establishment of a free trade zone in the Pacific region. This would be home to half the world's population and generate half the world's economic output.
The Organisation of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) was founded in Baghdad in 1960 by Iraq, Iran, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia and Venezuela, later joined by Libya, Nigeria, Algeria and the United Arab Emirates, among others. OPEC is based in Vienna. It represents the interests of the