Namibia - Economy and nature conservation today
History and countries
978-3-14-100890-6 | Page 145 | Ill. 6
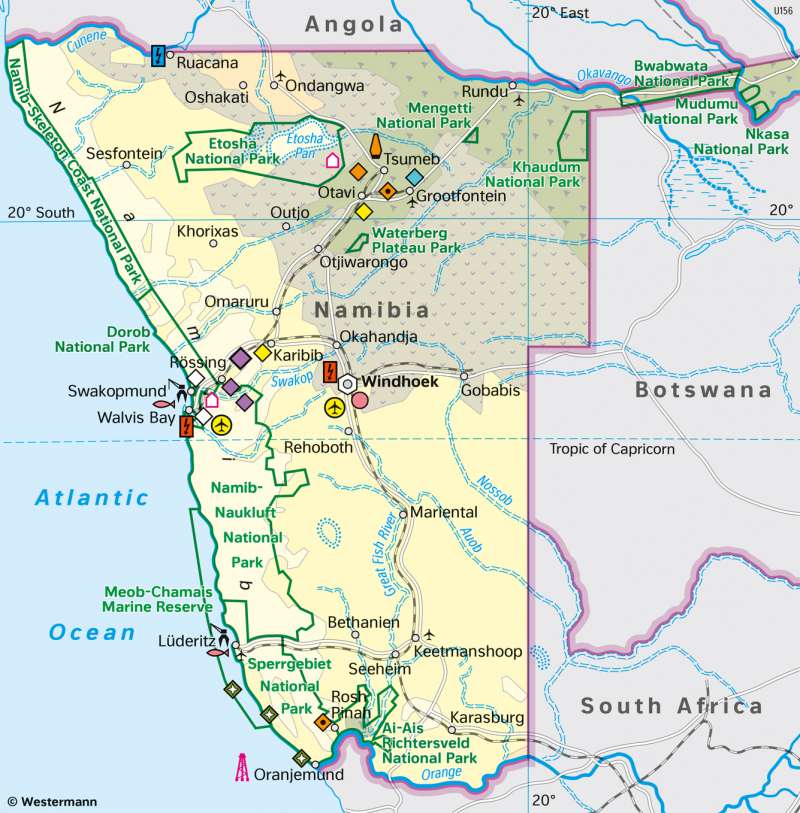
Overview
Namibia's landscape is essentially characterised by two deserts. On its west coast is the Namib, which stretches from South Africa to Angola, and in its east is the Kalahari. In between lies an inland highland of around 1700 metres.
The very sparsely populated country has a comparatively well-developed infrastructure and great wealth of mineral resources, including diamonds, natural gas, copper, zinc and uranium.
Namibia today
The Rössing mine northeast of Swakopmund is one of the largest uranium mines in the world. Diamonds, copper, and uranium alone account for about 40 percent of the export volume. In addition, fishing or fish processing and agriculture play an important role. Agricultural products such as fish, beef and pork and cultivated fruits, especially grapes, are among the most important export goods. About half of the exports go to Europe and about a quarter to countries in the Southern African Customs Union (SACU).
According to the Human Development Index, Namibia is one of the countries with medium human development, comparable to Morocco or Nicaragua. Namibia also has great tourism potential due to its scenic beauty and national parks, which gives this sector increasing economic importance.