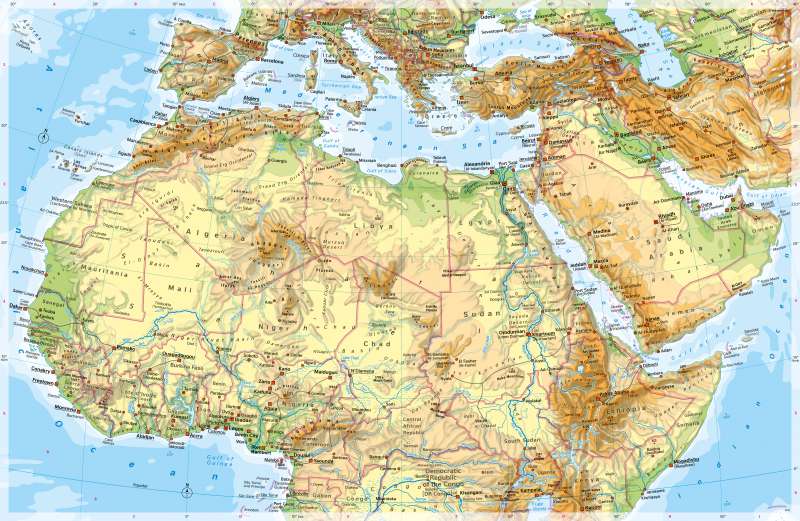
Northern Africa - Physical map
Physical map
978-3-14-100890-6 | Page 152 | Ill. 1
Overview
The map shows the large dry areas of northern Africa and western Asia and the rivers such as the Senegal, Nile, Chari, and Niger as the lifelines of these areas. Together with the coasts, they are guidelines and points of concentration for settlement in the north of the continent. South of the Sahara, the settlement pattern becomes more uniform in the alternating humid and ever-humid tropics. From the Mediterranean or the Atlantic, the surface rises towards the interior of Africa, the only exception being the Atlas. More or less broad sedimentation areas lie along the coasts. Inland, there are initially extensive erosion areas with wide plateaus and strata. Finally, in the interior of the continent, large-scale basins and mountain sills, some of which have the character of high mountains. While the young alpine mountain building was effective in the Atlas, large parts of North Africa are geologically quite old. The greatest heights in northern Africa are reached in the eastern highlands and mountains, in the Atlas Mountains and the central Saharan mountains (Ahaggar, Tibesti). The highlands of Ethiopia connect the rift system of East Africa with that of the Red Sea like a hinge. It has distinct altitudinal levels of vegetation and use.
Sahara and Sahel
With around nine million square kilometres, the Sahara is the largest desert on earth - around 25 times the size of Germany. It can be divided into three sub-regions from west to east:
- the wide, relatively low coastal plains and plateaus in the west, - the high mountain massifs of Ahaggar, Aïr, and Tibesti as well as the large plateaus and basins bordering to the north and south in the centre and - the, again, relatively low plateaus and basins in the east, which are crossed by the river oasis of the Nile.
The border of the Sahara in the east is formed by a mountain range parallel to the coast of the Red Sea.
South of the Sahara, elongated sills mark the transition to the Atlantic coast (Upper Guinea Sill in West Africa) or to the Central African Congo Basin. The water system is aligned with the basins (cf. rivers to Lake Chad, Upper Nile Basin [Sudd], Congo Basin). Wadis and salt pans are examples of the typical range of forms of the great deserts.
The dashed outline of Lake Chad, which has lost a large part of its surface area as a result of anthropogenic influences and persistent droughts, is striking. The shoreline of the very shallow lake changes its position annually according to the amount of rainfall in the region and the inflow.
Another striking landscape is the inland delta of the Niger River in Mali near Mopti. It is characterised by the seasonal flooding of the Niger and its tributaries, as well as by an extensive network of waterways.
Special features
- The highest mountain on the map is Mount Elbrus in the Caucasus (5642 m), in Africa it is Mt Kenya (5199 m) south of the highlands of Ethiopia.
- In the Sahara, numerous wadis (dry valleys in which water rarely flows) can be seen. To be distinguished from these are seasonally flowing rivers, for example in Sudan.
- In the north of the Sahara, salt pans are visible in some places.
- Lake Chad has a variable shoreline.
- The Niger runs in a wide arc towards the interior of the continent, then turns south at Gao and breaks the Upper Guinea Threshold on its way to the Atlantic Ocean in Nigeria.
- At 6852 km, the Nile is the longest river on earth.
- The Nile and Niger deltas have typical characteristics of a delta estuary.
- In North Africa, some areas are significantly below sea level, notably the Kattara Basin at -133 m and the Melghir Shelter at -30 m.
- Significant historical sites or ruins are mainly located along the Nile (Pyramids of Giza, Thebes, Abu Simbel).
- Large reservoirs are located in the area of the Upper Guinea Threshold. Lake Volta, for example, occupies an area about half the size of Wallonia. It is thus the largest reservoir on earth.