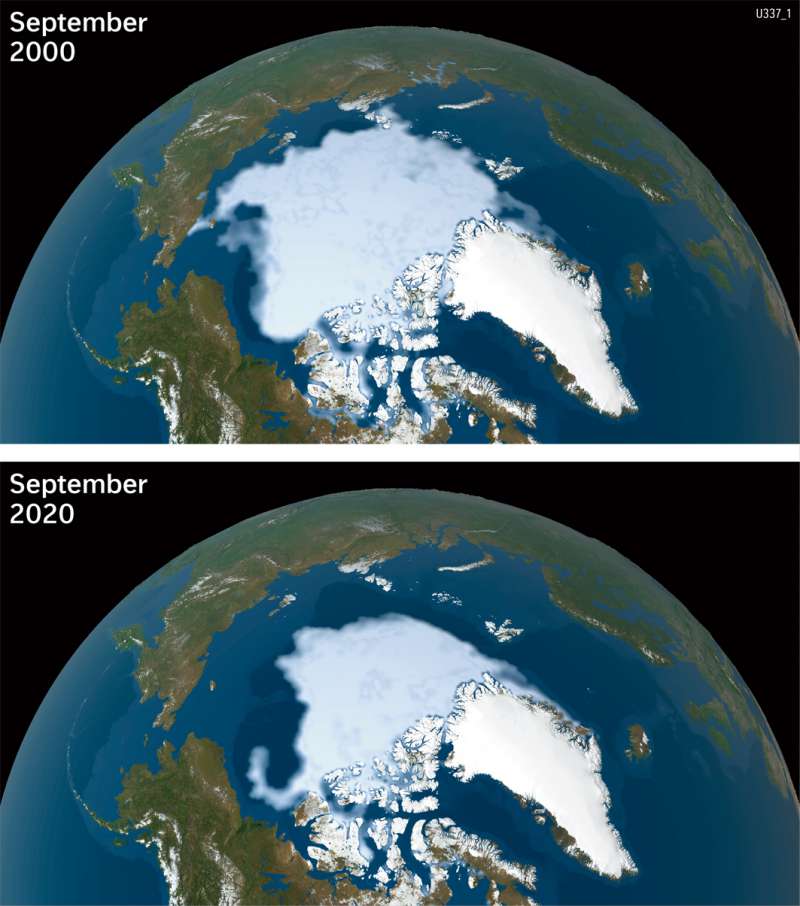
Arctic - Sea ice in decline
Human activities and environmental change
978-3-14-100890-6 | Page 201 | Ill. 5
Overview
In no other region of the world the consequences of climate change are as evident as in the Arctic. One of the most striking features is the change in sea ice extent. Its area also fluctuates for natural reasons. For decades, however, a strongly decreasing ice cover has been visible (as illustrated by the comparison between 2000 and 2020), which cannot be approximately explained by natural factors alone.
Decline of ice-albedo
Sea ice influences the Earth's radiation balance, but also has a considerable influence on the heat exchange between the atmosphere and the ocean and thus plays a decisive role in the global climate. Its decline is accelerated by the "ice-albedo ". Bright surfaces like sea ice have a large albedo. When sea ice retreats as a result of global warming, the albedo decreases. This makes more solar energy available, which leads to additional warming, which accelerates melting. This process mainly affects the ice margins - where the seawater warms fastest - and drives the "downward spiral": the lower the ice cover and thus the albedo, the greater the dark ocean surface and thus the melting effect.